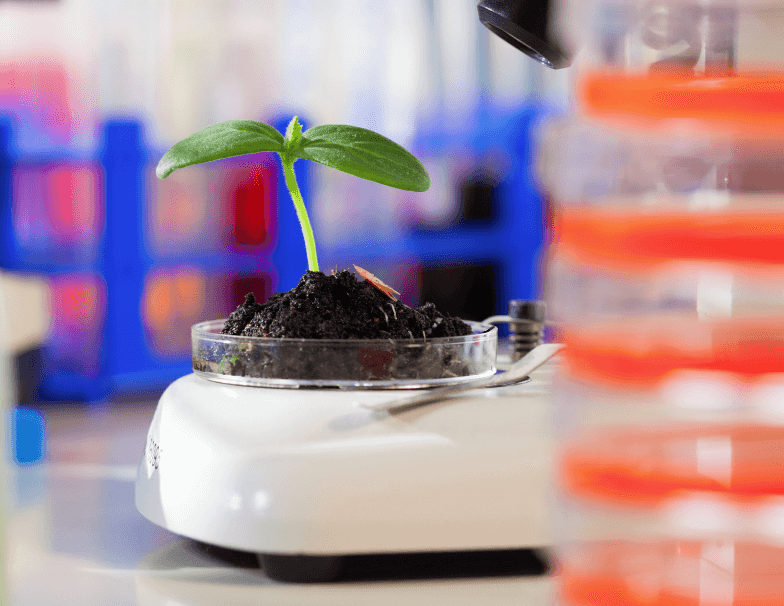
Biotechnology uses a set of techniques to modify living organisms or transform those of organic origin or using biological processes. Its most common uses are in industry, specifically in the agri-food industry, in health and in the environment. In this article we deal in detail with biotechnology in the food industry, from its definition to its applications with some examples.
What is food biotechnology?
Food biotechnology is the discipline that deals with the design, production, modification and evaluation of biological systems and living organisms in food.
According to the Spanish Society of Biotechnology in its document ‘Biotechnology and food’, food biotechnology is “the set of techniques or processes that use living organisms or substances that come from them to produce or modify a food, improve the plants or animals from which the food comes, or develop microorganisms that intervene in the processes of its elaboration”.
As this organism indicates, most of the foods of our daily consumption, both plants and animals, have undergone some biotechnological transformation to obtain that product that will reach the market for different reasons such as:
- Production needs
- To improve their nutritional properties
- To change their sensory qualities, such as smell, taste, texture or shape.
As indicated by the World Health Organization, genetically modified foods are derived from organisms whose DNA (genetic material) has been modified in a process that does not occur naturally. For the organization, in the future it is likely that this genetic modification will be aimed at “altering the nutrient content of foods, reducing their allergenic potential or improving the efficiency of food production systems”. In any case, they insist that all these genetically modified foods are evaluated before entering the market, so that those available have been “subjected to safety evaluations and no effect on human health has been detected as a result of their consumption”.
Is a GMO the same as a transgenic?
A genetically modified organism (GMO) is an organism that has undergone an artificial alteration in its genetic material. Transgenics fall into the GMO group, but they are part of a smaller group to which exogenous DNA has been introduced, that is, DNA that does not belong to the original genome, as this article makes clear.
Biotechnology in the food industry
Nowadays, technology and science are related to food to improve its quality, to contribute to its productivity, to improve its health properties (for example, probiotics) or to obtain foods that have a lower environmental impact.
Many of the new foods are designed to improve health in some specific area, since it is possible to modify the composition of a traditional food and increase its nutritional value, for example, in essential amino acids or vitamins.
At INFINITIA we have a team of professional experts in food technology and a specific laboratory to conduct training sessions for tasters. Within the area of innovation in materials, the technologists and engineers that make up the group focus on providing their knowledge and technological capabilities to the production chain and market introduction, taking into account factors such as:
- Quality of new foods
- Nutritional values
- Profitability
- Product optimization
Here you can learn how engineering is capable of improving foodstuffs.
Biotechnology and food safety
In the industry, legislation is very demanding in terms of food safety with nutritional and toxicological tests, both for GMO and non-GMO foods. In the group of foods known as novel foods, it is necessary to study the nutritional, toxicological and allergenic consequences. It is also necessary to evaluate “the biochemical characterization of the food and the precise characterization of the genetic modification incorporated in the GMOs, including the site of insertion in the genome, the number of copies and the level of expression of the genetic material introduced”, as indicated by the Spanish Society of Biotechnology.
Biotechnology applications in the food industry
Biotechnology has traditionally been present in food processing, in the production of everyday products such as bread, wine or cheese.
So-called modern biotechnology, in which living cells are genetically modified, is mainly applied in agriculture in three ways:
- Agronomic applications: from increasing production to pest resistance.
- Nutritional applications: modification of their composition to obtain, in general, foods with specific healthy characteristics.
- Component modification: such as color, flavor or aroma.
Practical examples of the application of biotechnology in the food industry
Determination of microbiological evolution during fermentation
INFINITIA faced the challenge of finding out what happens in the culture of microorganisms in the different phases of a bread during fermentation. To address this challenge, the team designed a methodology adapted to the preparation of the dough in different phases and performed a microorganism culture, choosing different points of each stage.
Evaluation of the antimicrobial properties of a device for food disinfection
The challenge consisted of evaluating the disinfectant capacity of a device on certain foods. To do this, the methodology had to be adapted to simulate the real conditions of use of the device in order to identify the variables with the highest antimicrobial capacity on food surfaces. Here you can learn more about this success story.
Would you like to count on the help of our laboratory for an application or evaluation related to biotechnology? Contact our team.