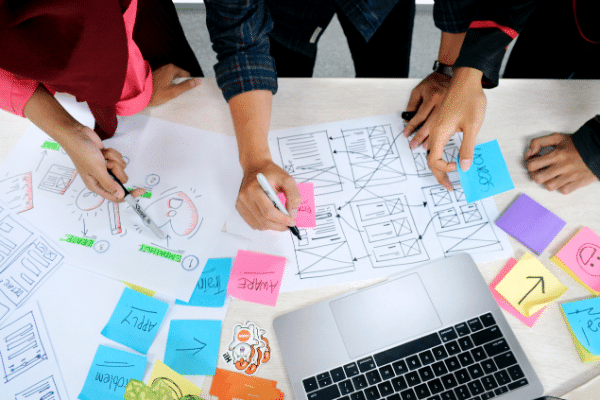
The Design Thinking methodology makes it possible to address any challenge faced by industrial design and generate successful solutions, thanks to innovative thinking. In this article, we will explain what it is and what are the Design Thinking phases necessary to put it into practice.
What is Design Thinking?
Design Thinking is a design methodology based on an iterative approach to thinking, which serves to solve problems with innovative solutions. It is extremely useful in addressing complex, ill-defined or unknown industrial problems by understanding the human needs involved, reframing the problem, creating feasible and effective ideas and adopting a practical approach through the development of tested prototypes.
Design thinking methodology aims at user-centered, complex problem solving. In addition, it seeks to obtain practical results, tangible products or processes that are:
- Technically feasible and functional.
- Economically feasible.
- Desirable for the user
Design Thinking Phases
The Design Thinking methodology consists of five steps which are as follows:
1. Empathize
The Design Thinking methodology starts with empathy. To create innovative products, it is necessary to understand who the users are and what they need. What are their expectations of the product being designed? This first phase consists of gaining an empathetic understanding of the problem by observing, engaging and empathizing with people to understand their experiences and motivations. Therefore, the design team will need to broaden their assumptions and delve into the vision of the users and their needs.
2. Define the problem
Second, the information gathered during the empathy phase is gathered. It is then analyzed and synthesized to define the main problems identified by the development and design team.
The Design Thinking methodology approaches problems from a user and human perspective and does so in an iterative manner. For example, to identify a new business opportunity in the beverage industry, instead of focusing on problems from a business desire of its own, the approach consists of an in-depth strategic industry analysis and extensive user research.
3. Generate ideas
This stage of the process consists of ideation, i.e. thinking about possible innovative solutions from the point of view of non-linear thinking.
When coming up with innovative ideas, the design and prototyping team meets and explores possible solutions, approaching them from different angles and in a creative way. Thanks to the above steps, it is possible to approach design and industrial development problems from an alternative perspective.
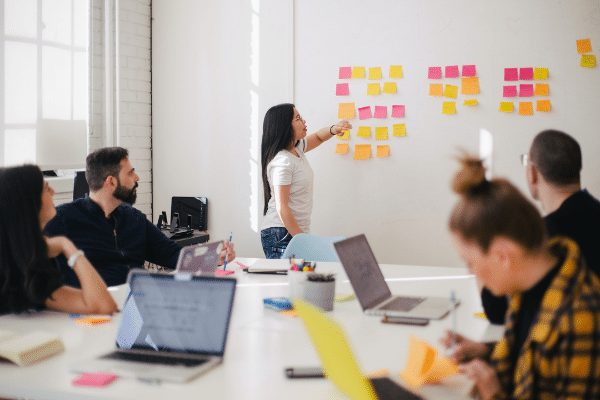

4. Develop prototypes
The fourth stage of the process is strategic design and prototyping. This is an experimental phase, the objective of which is to generate the best possible solution for each of the problems identified during the first three stages. This is the time to create industrial prototypes that put the design ideas into practice, make them tangible and test their effectiveness.
The design team will produce a series of reduced and inexpensive versions of the product, or of specific product features, in order to investigate the solutions that are implemented in the prototypes.
5. Test the design prototypes
In the fifth Design Thinking phase, the various prototypes are tested, investigated and improved on the basis of user experiences. In this way, you get a better idea of how real users behave when interacting with the final product. Similarly, any design flaws are also revealed, which can be resolved by going back to earlier stages of the process.
In conclusion, the Design Thinking methodology presents a creative and innovative perspective when developing new components, materials or industrial products that guarantee success in their design and user satisfaction. Do you want to design a new product or develop a new material and need expert advice? Contact our strategic design and prototyping team and they will inform you without obligation.